Quick Start Guide
Visualization services Create a high rendering digital twin platform, committed to becoming a BIM/CIM 3D visualization tool.
Capable of data processing, scene integration, cloud service release, data sharing, two/three dimensional visualization, editing, cross-platform secondary development, industry applications, etc. To provide users with a plugin-free, cross-platform, cross-browser complete solution from the original data to the final 3D presentation, improving performance, effect, ease of use and interactive experience.
From enterprise architecture to digital infrastructure, from smart parks to smart cities, an enterprise-level digital twin platform that integrates operational big data provides a holistic visual blueprint for digital enterprises.
Getting Started Guide
Prerequisites
When using the DTS Digital Twin platform, ensure that the relevant software is downloaded and installed.
Licensing
Launching and using DTS Digital Twin platform requires installing hardware or software license and running the CodeMeter service.
Running the program without the hardware encryption lock will pop up an error message.
Note: To obtain the hardware encryption lock, please contact the relevant department of Freedo Technology or apply on the official website of DTS.
Procedure
After meeting the above conditions, please perform the following procedure to use the digital twin platform.
Operation Process
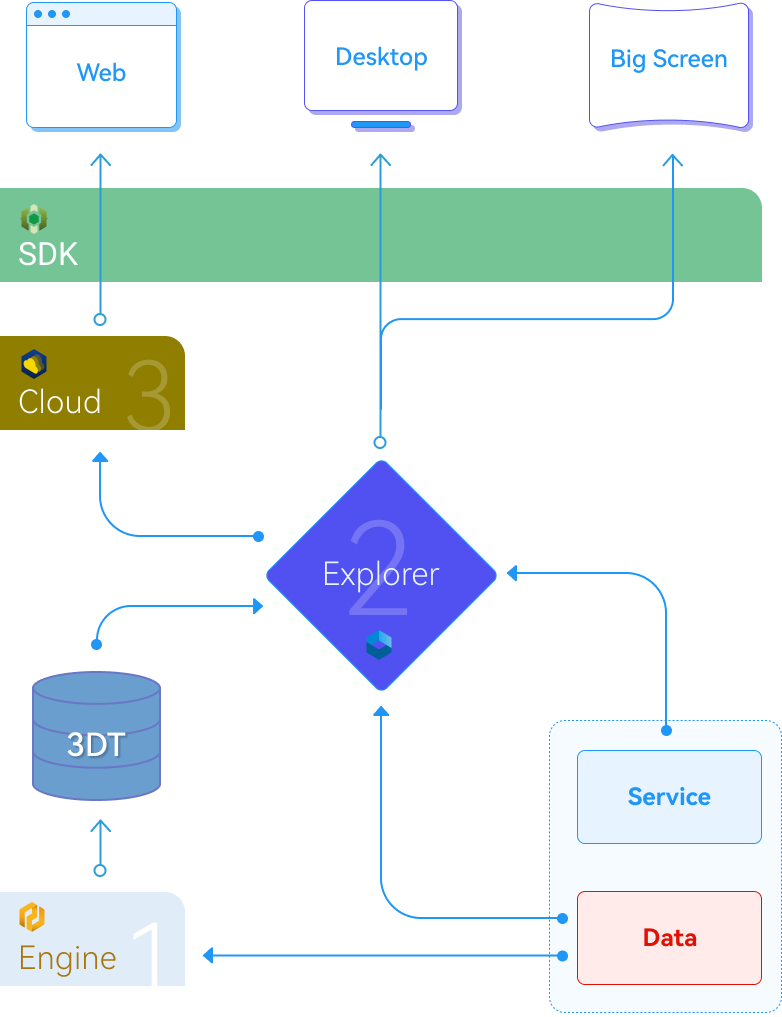
The visualization product provides a complete solution covering processes such as data conversion, integration, cloud publishing, and secondary development.
Engine processes multi-source data.
Explorer integrates and edits the processed data.
Cloud publishes the organized scenes as cloud service video streams, enabling multi-platform access.
Operating instructions
Data handling
Engine is a multi-source data automatic processing tool for high rendering platform, supporting a variety of data formats and types.
Operating Instructions
Terrain images, tilt photography, point cloud data, model data, and BIM data need to be processed into H3D data files by Engine publishing. H3D can optimize and accelerate the data, and enhance the user's operating experience in the high rendering platform.
Aconf configuration file, which can save data release and processing related information, including data, settings and other information content. By loading the configuration file, you can quickly resend or resend data. It is mainly used for some unexpected situations that cause publishing interruption.
Publishing terrain images
Step1 Open Engine and select the "Terrain Images" category.

Add DOM (image) and DEM (elevation) data. And whether to "Enable invalid value for seamless splicing" (You must select this option when publishing multiple images). The relevant parameters are shown in Table 3-1.

| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Image (DOM) | Input the image data to be published. "File" loads a single file, while "Directory" loads all data of the same type in the directory (including subfolders). |
| Elevation (DEM) | Input the elevation data to be published. "File" loads a single file, while "Directory" loads all data of the same type in the directory (including subfolders). |
| Enable Invalid Values | Select this parameter to enable invalid values in terrain imagery when publishing. |
| Note | Multiple image publishing requires selecting "Enable Invalid Values." |
| Altitude Filling | When this parameter is selected, regions with no values in the elevation data are automatically filled with altitude values. |
| Note | If certain regions of the elevation data lack height values, select this parameter to manually set a height value (default is 0), avoiding adjustments to the original data. |
| Outer Clip Polygon | Clips the external terrain portions of vector data. |
| Inner Clip Polygon | Clips the internal terrain portions of vector data. |
| Hydrography Polygon | Converts the terrain corresponding to vector data into highly realistic dynamic water. |
| SHP Offset | Sets the offset value for clipping vector data. |
| Ocean Parameter Settings | Sets the relevant parameters for the ocean range in the terrain. |
| Feathering Range | Sets the feathering transition range for external elevations. |
| Overlap Range | Sets the overlap range of the DTM and the peripheral terrain imagery. |
| Depression Value | Sets the depression height for the central overlap area of the DTM and terrain imagery. |
| Depression Feathering | Sets the transition range for the depressed overlap area of the DTM and terrain imagery. |
| Feathering Range | Sets the feathering transition range for external elevations. |
| Number of Parallel Publishing Processes | Specifies the number of processes occupied by Engine during publishing. A higher value increases the number of processes and improves publishing efficiency. The range is 0–50. |
| Character Interaction Collision | When enabled, supports collision with terrain and imagery models in Explorer's 3D scenes during flight and walking interaction modes. |
Select the file output path and name the database for publication.
Select "Save" to store the publishing profile. Click "Save" to store the publishing configuration file.
After the file is stored, click "Start Publishing" to trigger a prompt message.
After confirming everything is correct, select "Yes" to execute the publishing operation.
Post Oblique Photography
Open Engine and select the "Oblique Images" category.
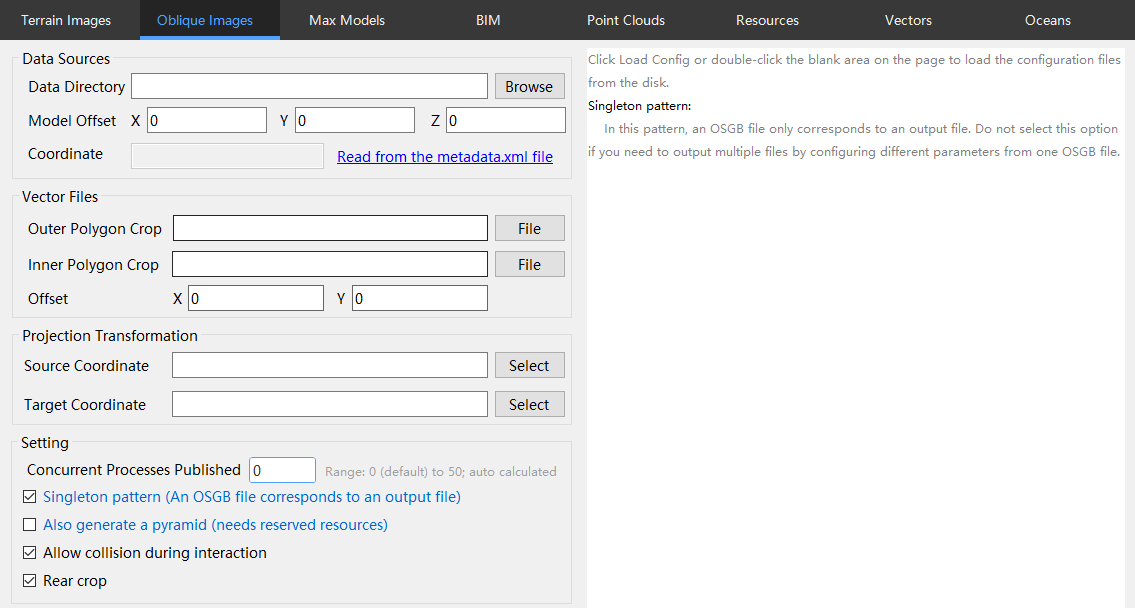
Add oblique photogrammetry data and set the relevant parameters for publishing. For detailed parameter descriptions, see Table 3-2.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
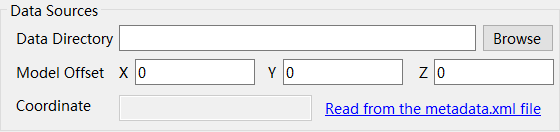
| Model Offset | Coordinate offset value for the oblique photogrammetry data, which can be obtained by loading the "Metadata.XML" file. |
| Source Coordinate System | Select the coordinate system PRJ file of the data source. |
| Target Coordinate System | Select the target coordinate system PRJ file. |
| Outer Clip Polygon | Clips the external terrain portions of vector data. |
| Inner Clip Polygon | Clips the internal terrain portions of vector data. |
| Shp Offset | Sets the offset value for clipping vector data. |
| Number of Parallel Publishing Processes | Specifies the number of processes occupied by Engine during publishing. A higher value increases the number of processes and improves publishing efficiency. The range is 0–50. |
| Singleton Mode | If the same set of oblique photogrammetry data needs to be processed multiple times into the KooMap platform, selecting this parameter may lead to a failure in scheduling. |
| Synchronize Pyramid Generation | Generate pyramids simultaneously while publishing tiles to reduce total publishing time. |
| Note | High requirements for the computer; enable based on actual conditions. |
| Note | High requirements for the computer; enable based on actual conditions. |
| Character Interaction Collision | When enabled, supports collision with oblique photogrammetry models in Explorer's 3D scenes during flight and walking interaction modes. |
| Backface Culling | Removes the backface model of the oblique photogrammetry model to reduce the model's data size. Enabled by default. |
| Lightweight | Enables lightweight mode, which simplifies the 3D model details, reduces texture resolution, and removes unnecessary geometric data, making objects or models in the scene lighter and reducing memory and computational resource consumption. |
Select the output file path and specify the database name after publishing.
Select "Save" to store the publishing configuration file.
Select "Start Publishing" and a prompt message will appear. If everything is correct, select "Yes" to execute the publishing operation.
During the publishing process, a command-line window will pop up and remain open until the publishing is complete.
When the publishing is complete, the information window will display a message indicating that the publishing has finished.
Release Max model
Open Engine and select the "Max Models" category.
Set the output path of the H3D database after publication.
Click "Directory" or the button on the right of "Directory" and select "Add Oblique Model OSG Directory" or "Add OBJ Directory" to add Max model data; click "Add File" to add Max model data.
Select the data from the data list and set the type. The type should be selected based on the actual type of the model. Choosing the appropriate type will optimize the data. The specific types are shown in Table 3-3.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Building | Textured building model without interior. |
| Interior | Textured building model with interior. |
| Building Mass Block | Untreated white model without texture. |
| Ground | Roads, bridges, green spaces, etc. |
| Water System | Plants. |
| Tree | Plants. |
| Underground Pipeline, Small Items | Pipelines, pipe points, small items. |
Select "Save" to store the publishing configuration file.
Select "Start Publishing" and a prompt message will appear. If everything is correct, select "Yes" to execute the publishing operation.
Publishing the BIM model
Open Engine and select the "BIM" category.
Set the output path of the H3D database after publication.

Click "Directory" or "File" to add BIM model data. You can add different types of BIM data simultaneously.
You do not need to select an object to set advanced parameters. The BIM data must be set to the correct "Viewport".
Select "Save" to store the publishing profile.
Select "Start Publishing" and a message will be displayed. If you are sure, select "Yes" and perform the publishing operation.
During the publishing process, the information bar displays the current publishing information.
When the release is complete, a message indicating that the release is complete and successful is displayed in the information window.
Publish Point Cloud
Open Engine and select the "Point Clouds" category.
Set the output path of the H3D database after publication.
Add point cloud data.
Select "Save" to store the publishing profile.
Select "Start Publishing" and a message will be displayed. If you are sure, select "Yes" and perform the publishing operation.

A command line window will pop up during the publishing process until the publication is complete.
When the release is complete, a message indicating that the release is complete and successful is displayed in the information window.
Publishing Resources
Open Engine and select the "Resources" category.
Select "File" and select SHP file.
Set the output path of the H3D database after publication.
Select the "Height From"mode for the post-publication footage.
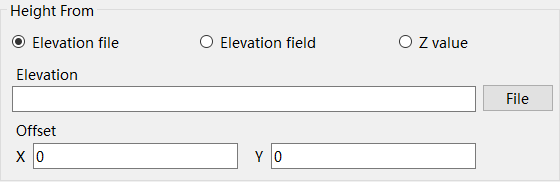
If you choose "Elevation file" mode, select the option to load the "Elevation" file.

Set the corresponding "Offset Value" (optional).
If you want to customize the object ID, you can fill in the field name into the input box.
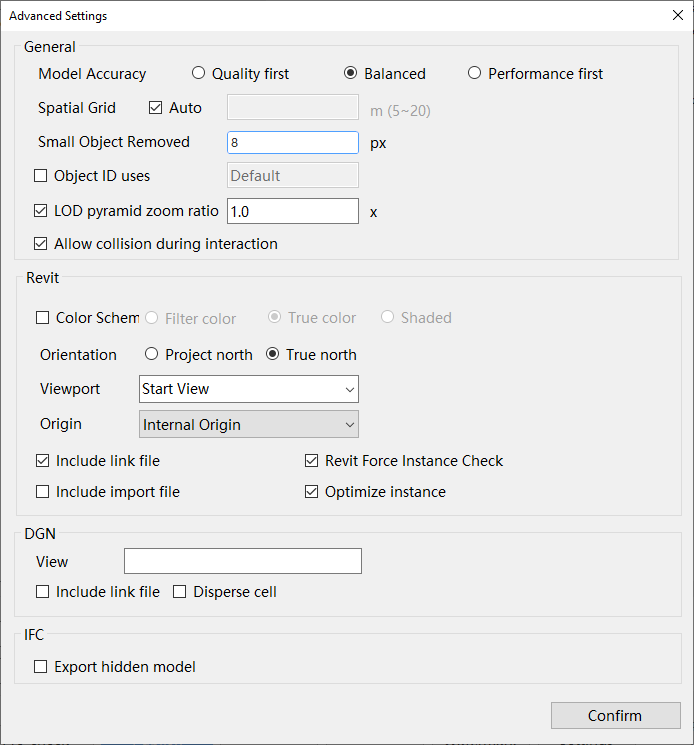
Select "Advanced Parameters". In the "Advanced Settings" panel that pops up, set the relevant parameters.
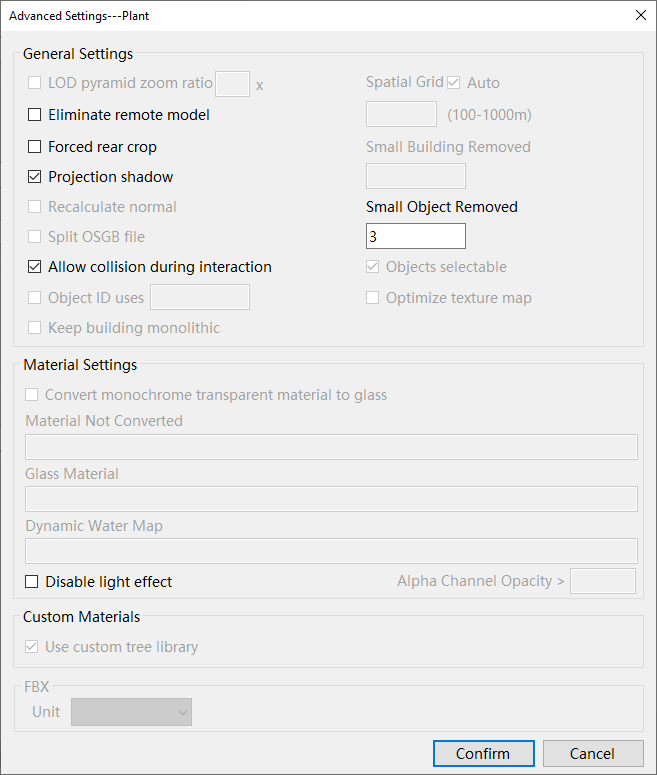
Select "Start Publishing" and a prompt message will appear. If everything is correct, select "Yes" to execute the publishing operation.
Publish vector
Open Engine and select the "Vectors" category.
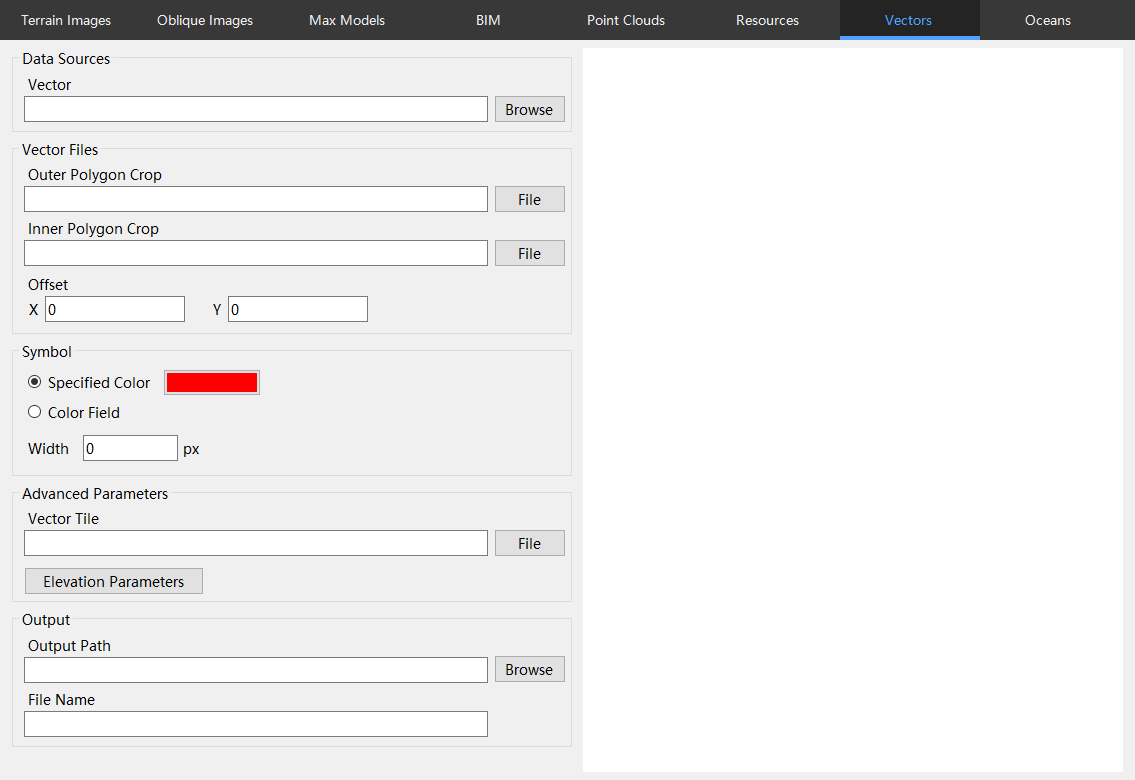
Add "Data Sources" and select either the vector SHP file (support line, surface) or VTPK.
If SHP needs to be clipped, add the corresponding SHP files in the external or internal clipping polygon section.
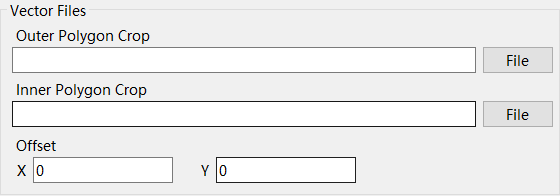
Set the symbol style, either by assigning a color to the SHP data, or by reading the color field to set the color of the vector data.
Set the elevation, pop up the "Elevation Parameters " settings panel, then set the image and elevation parameters.
If you want the published vector data to match the published terrain exactly, then the corresponding parameters should also match exactly.

Select "Start Publishing" and a prompt message will appear. If everything is correct, select "Yes" to execute the publishing operation.
Release of Marine data
Open Engine and select the "Oceans" category.
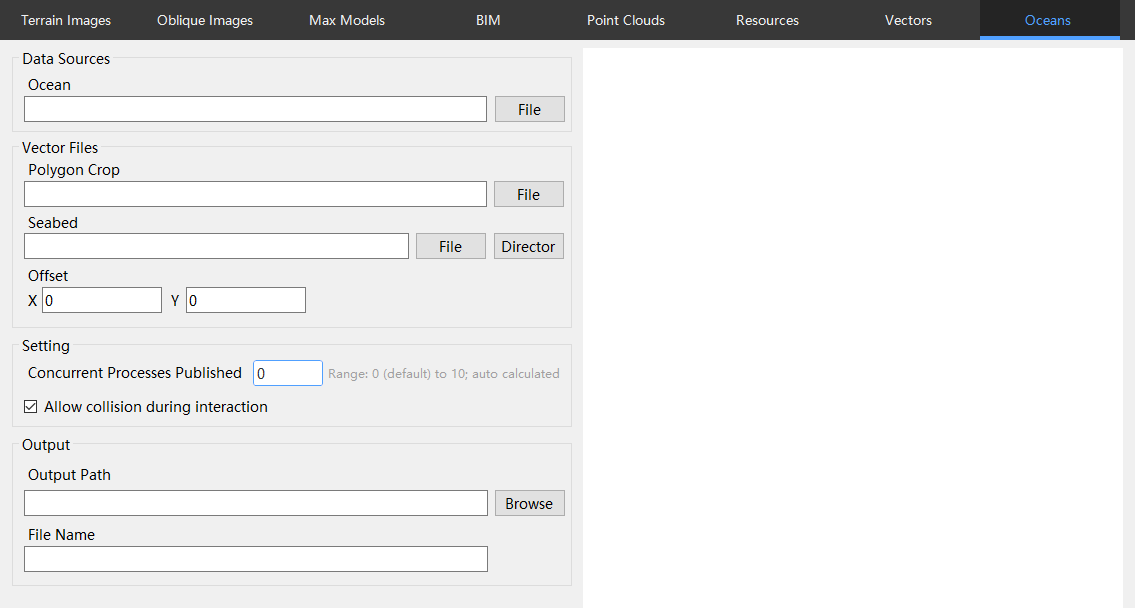
Add "Data Sources" and select the Ocean SHP file.
If SHP data needs to be clipped, add the corresponding SHP file in the clipping polygon field.
Add the sea floor elevation.
Set the output path of the H3D database after publication.
Save the publish configuration and select "Start Publish" to publish.
The publication is complete, and the corresponding H3D database file is generated.
Scene integration
Explorer is a builder and editor for digital twin scenes. H3D published by Engine can be integrated.
This chapter describes the basic usage of the Explorer.
Homepage Interface
After launching the Explorer, the homepage is displayed first.
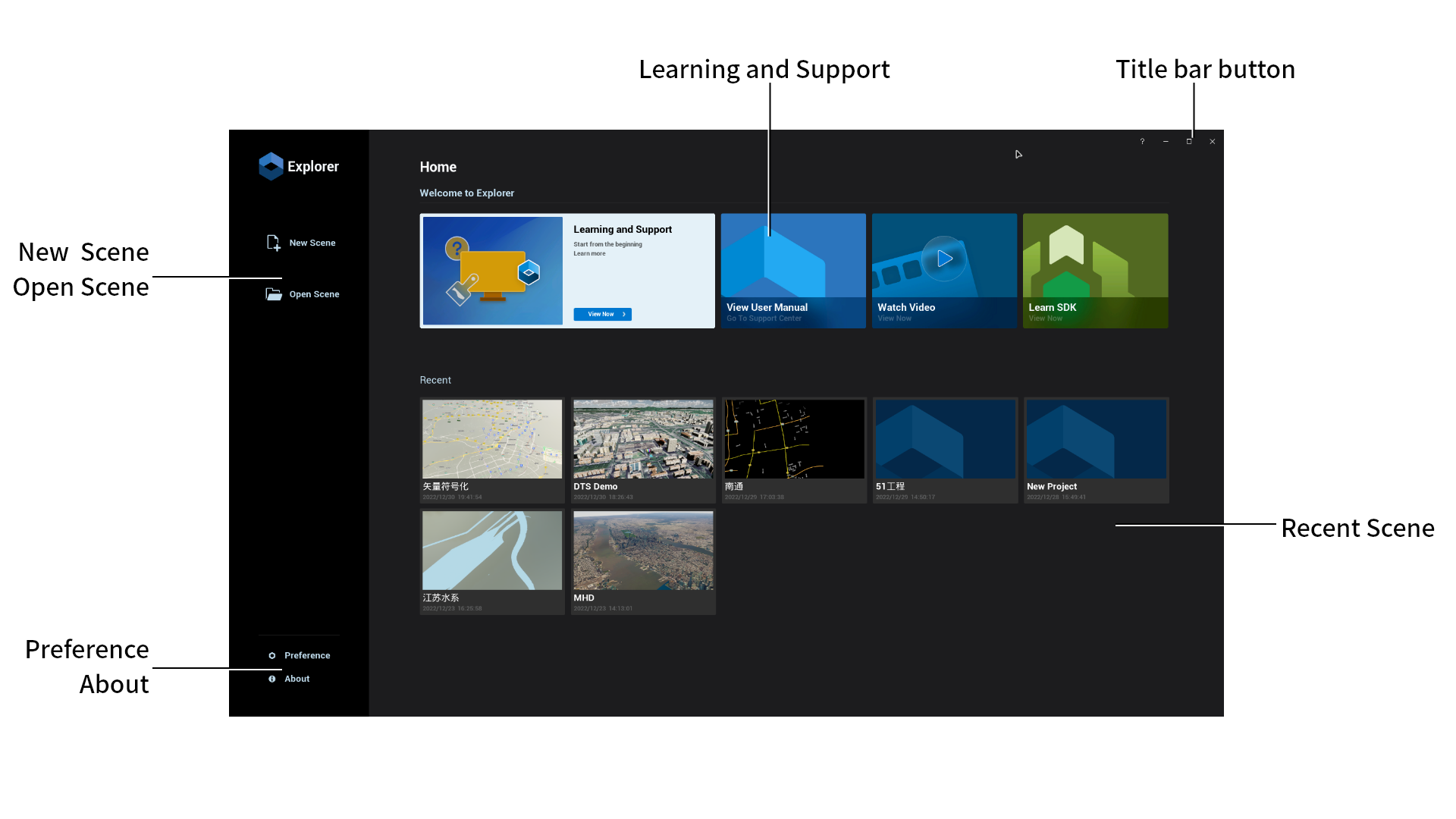
New / Open Scene
Create a new scene, or open a created scene. You can also quickly open a scene from the "Recent".
Welcome to Explorer
Contain links to learning support and user manual. You can quickly access the content with a click.
Recent
"Recent" can record the last 10 scene records. Hover over the scene thumbnail to view the full name and storage path.
Preference
Set scene automatic backup, library path and hotkeys of the Explorer.
About
View the version, update log, and more of the Explorer.
Operation Interface
The interface of the Explorer includes "Manager", "Toolbar", "Function Panel", "Scene Viewer", "Compass" and other contents.

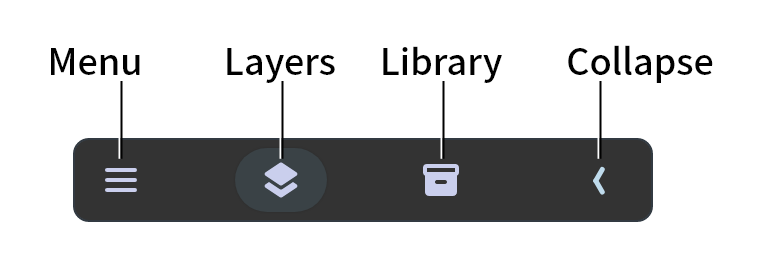
Manager
The "Manager" mainly includes "Layers" and "Library" two parts, click on the button to switch. The "Menu" includes operations of "Scene", "Preference" and "Help". The "Collapse Button" can expand or collapse the Layer Panel.
Toolbar
The "Toolbar" is a collection of tools. Each "Tool" represents a category of function menu.
Function Panel
The "Function Panel" contains the functions and parameters of the tools. The contents of panel are automatically adjusted depending on the tool.
Compass
The "Compass" is a tool for indicating direction. The red pointer points to the geographical North Pole and the white pointer points to the geographical
South Pole.

Transform Tool
Edit the position, rotation, and scaling of the objects.
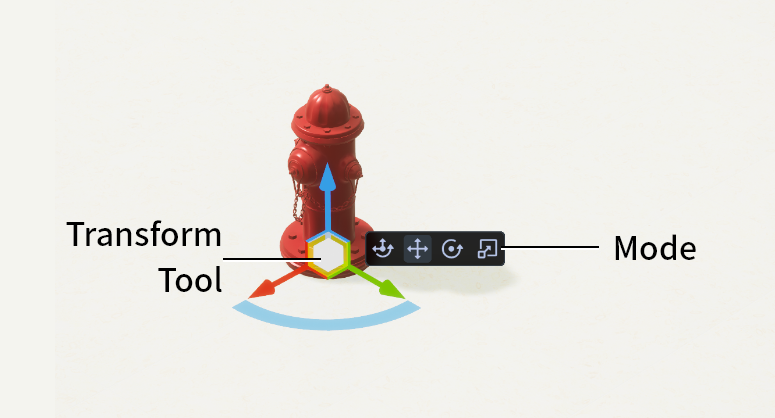
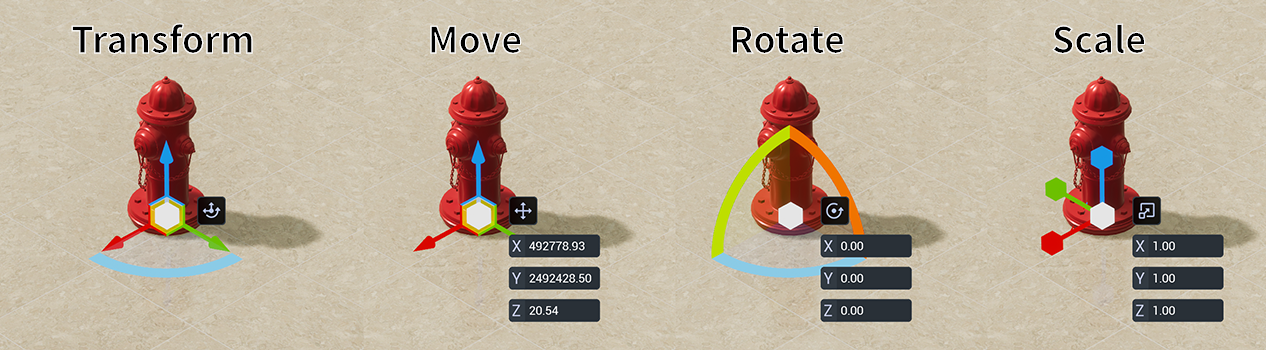
The Transform Tool has four modes, Comprehensive, Move, Rotate and Scale.
Configure Library
Configure PAK files to use various resource objects in the Library.
Operating steps
Launch the Explorer and click "Preference" in the bottom left corner of the homepage.
Click the "General" tab in the "Preference" panel.
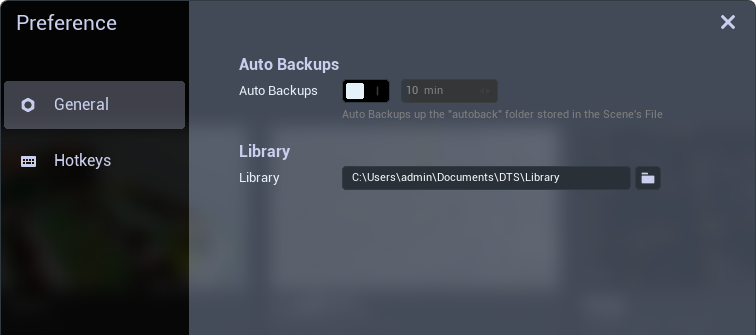
Set the storage path of the PAK files in the "Library".
Close the "Preference" panel.
Instructions
Some data and services rely on the project coordinate system.
If the coordinate system is set incorrectly, the coordinates of some services and data will display errors.
Configure resource files
Specify the path of the resource file (in PAK format) to ensure access to various resource objects in the resource library.
Procedure
Run the Explorer software, go to the lower-left corner of the homepage, select "Preferences" and in the pop-up "Preferences" panel, choose "General."
Set the storage path for the PAK resource package in the "Library" settings.
After completing the settings, close the "Preferences" panel.
New project
Create a new 3D scene project.
Procedure
Run the Explorer software and "New" and "Open" appear on the left side of the interface.
Select "New Project" or, in an already running program, choose "Project > New" to open the "New Project" panel.
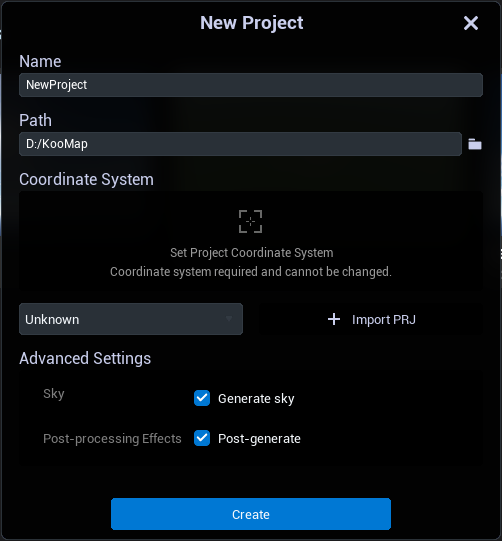
Enter the "name" of the project.
Select the path and set the "Path" where the project file will be stored.
Select a built-in coordinate system from the coordinate system drop-down menu. Alternatively, select a PRJ file.
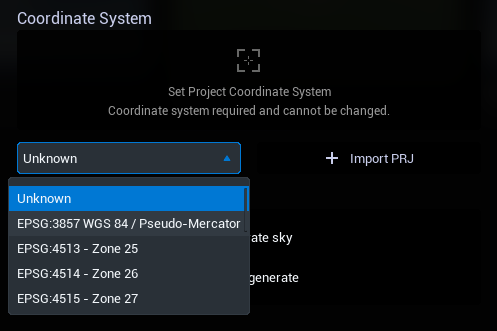
Only projection coordinate systems are currently supported. Only common coordinate systems are listed in the drop-down menu, other coordinate systems can be set by loading the PRJ file. When using the 3D Tiles service, the project must set the coordinate system.
Adjust "Advanced Settings" as required. In the current advanced Settings, you can select whether the project needs to "Generate sky" and whether it needs "Post-generation".

Select "create" to finish creating the project.
Open project
Open an existing 3D scene project.
Support ACP and DTML format scene project.
Procedure
Run the Explorer software and "New and "Open" appear on the left side of the interface.
Select "Open", or select "Project > Open" in a program that is already running. Pop up the resource manager.

Select ACP or DTML project file and open it.
Import H3D
Import the H3D file.
Procedure
Choose "Project > Import H3D" to pop up the Explorer.
Select the target file and click "Open."
When importing the H3D file, the "Import 3DT" panel pops up.

Supports importing multiple H3D files at the same time. ID supports customization.
Set the ID, transform and advanced settings parameters of the H3D file as required.
The imported object will appear in the layer tree.
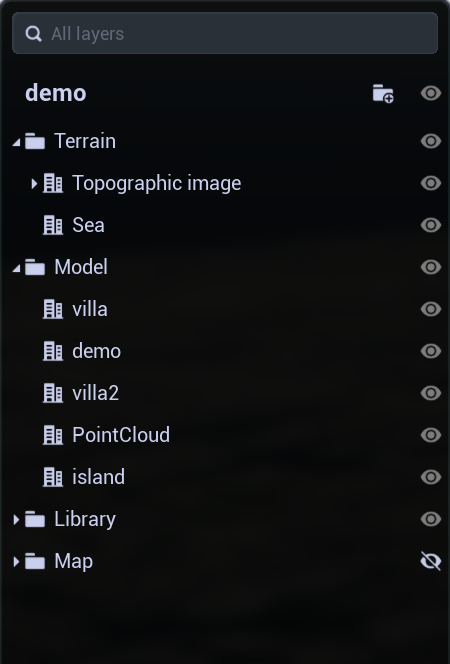
Import SHP
Add the ShapeFile file.
Procedure
Choose "Import > SHP" to pop up the Explorer.
Select the ShapeFile file.
When importing the "SHP" data, the "Import ShapeFile" panel will pop up. ShapeFile data can be set to "sign".
The imported object will appear in the layer tree.
Import 3D Tiles
Add 3D Tiles service. When adding the related service, make sure to set the coordinate system during the creation of the new project.
Procedure
Select "project > 3D Tiles", the add service panel will pop up.
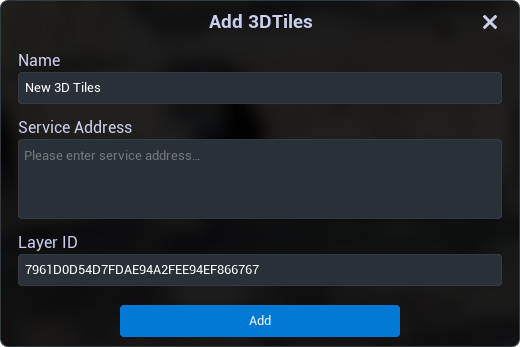
Set the name of the service.
Paste the URL path of the service address in the Service address box.
Set the ID of the service and select "Add".
The imported service will appear in the layer tree.

Use the guide
Create a new tour by taking key frames from several scene perspectives and concatenating them. Or create a non-linear keyframe animation.
The created tour or animation can be shown and played in "Report Mode".
Enter Debrief Mode
"Debrief Mode" is a mode for making presentations and presentations. In the bottom function panel of the debrief mode, all the guides in the project are displayed. In Report mode, the interface will change and interface elements such as "Layer Tree Panel" and "Toolbar" will be hidden.
Click the "Report Model" button at the bottom of the toolbar to enter report mode.
Environment Settings
Environment
The setting of parameters related to the environmental effect in the scene, including time, illumination, sun, moon, clouds, fog, rain and snow, ocean, etc.
Late
In post-production, you can adjust the contrast, saturation, flood light, ambient light mask, LUT color palette, filter effects and other parameters.
Camera
Adjust the relevant parameters of the camera lens such as horizontal viewing Angle, lens halo, dark Angle, rain and snow effect, depth of field, etc.
Using Tools
Measure
Basic measurement is mainly about getting the mid-point or quantity information of the scene. These include: coordinate measurement, linear measurement, horizontal measurement, vertical measurement, and area measurement.
Layers
Flattening, burrowing and other layer operations on terrain images and oblique photography data.
Dissecting
Make cutting observations in the scene, including surface cutting, body cutting and polygon cutting.
Queries
Click the property information of the query object and hide the object. Connect to the PostgreSQL database to view the detailed property information of the component.
Creating a resource
Through the resource function, you can create various resource objects in the scene, as well as edit and adjust the material.
Material editing
Material editing is mainly used for editing and replacing the texture of the model material.

Vegetation
Add ecological resources such as flowers and trees to the scene.

Means of transportation
Add vehicle-type vehicles to the scene. Such as trucks, cars and other vehicles,
and can automatically simulate the driving situation of vehicles. The vehicle
also supports night and day light switches.

Water
Quickly create dynamic water objects in the scene.

Video projection
Project a video frame onto an object in the scene.
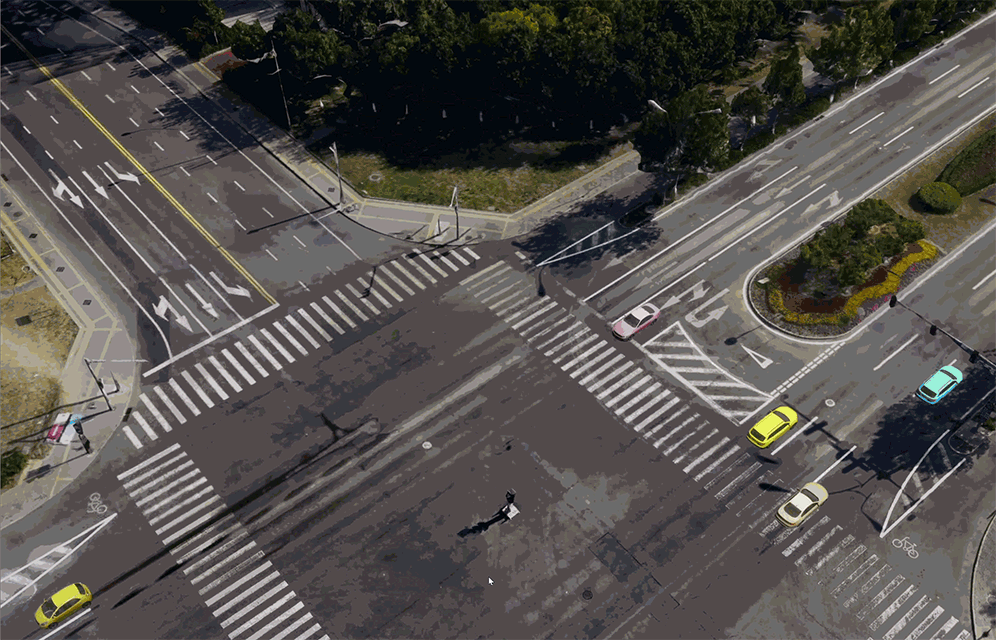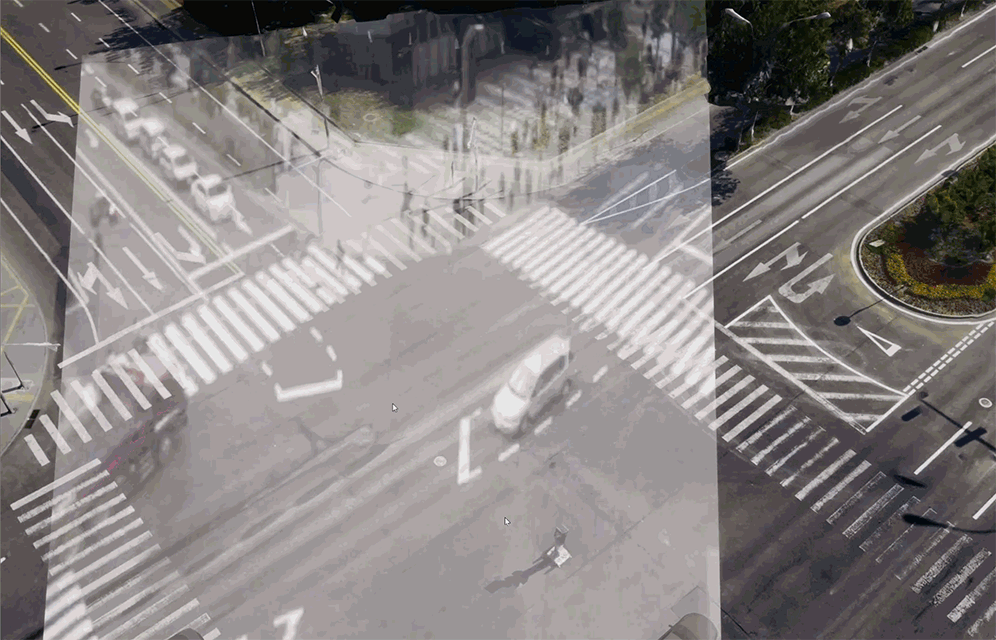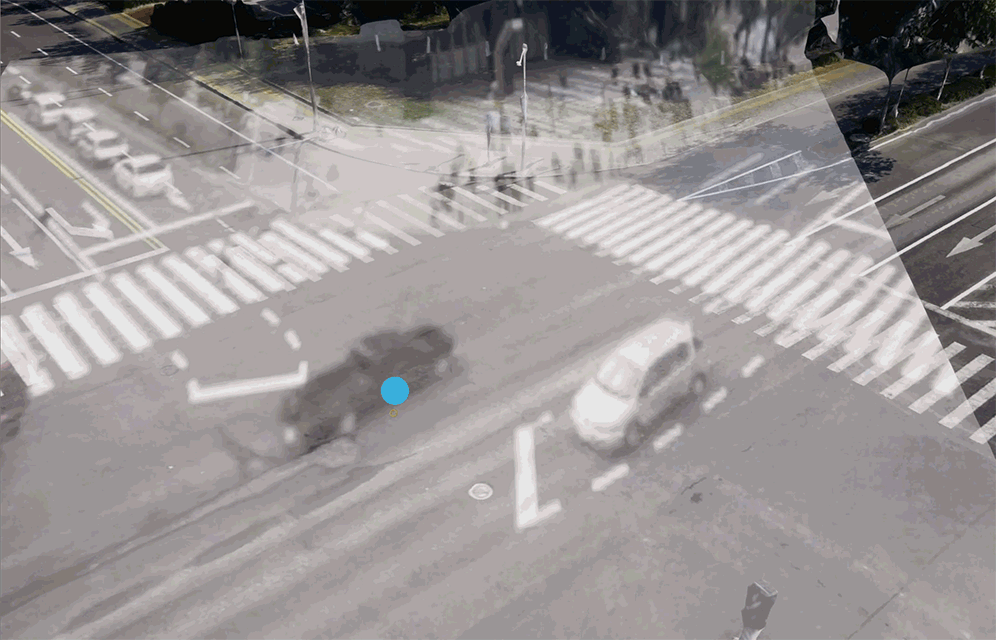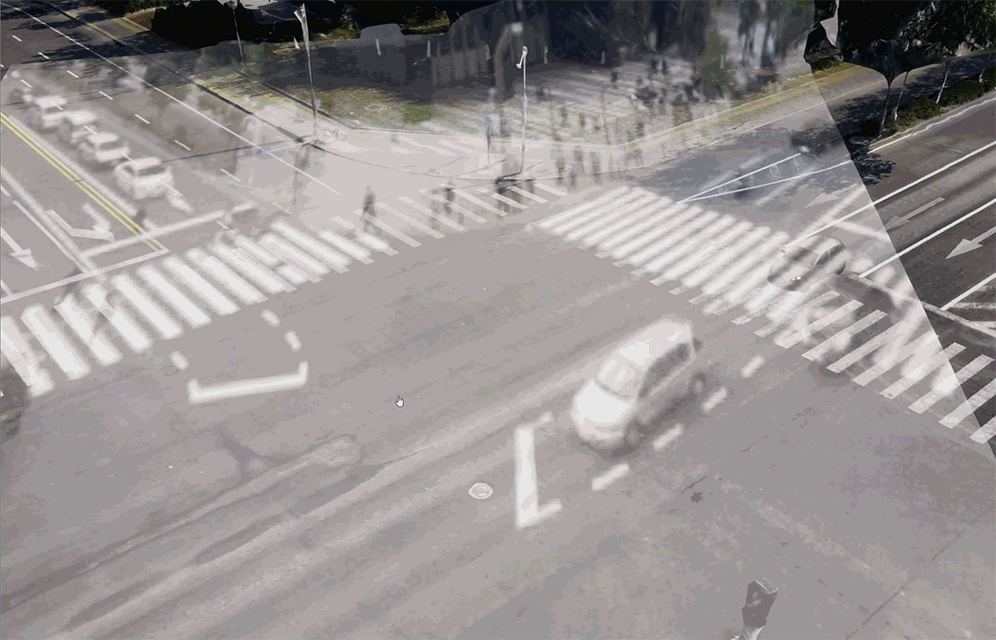
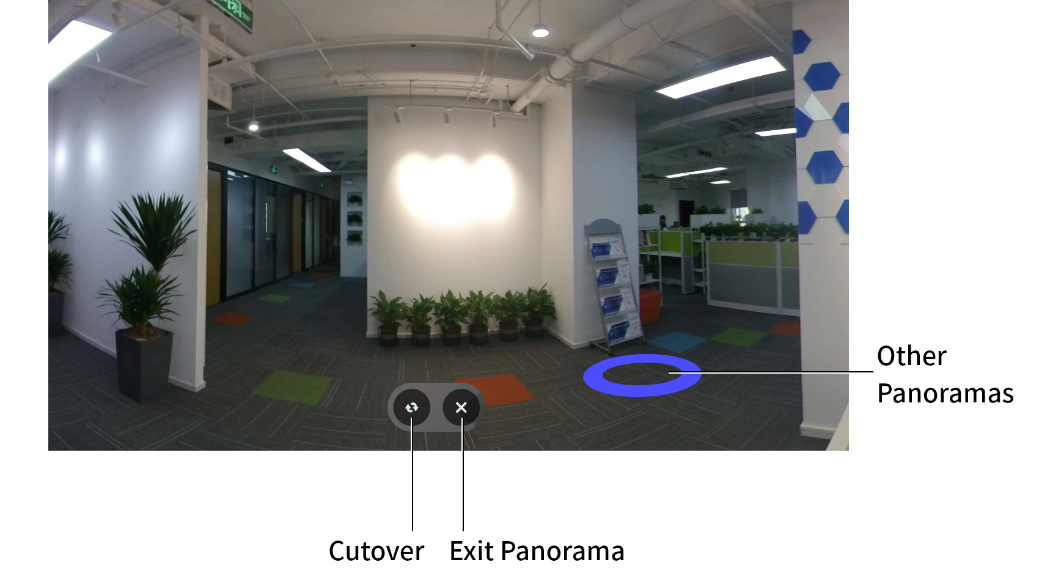
Panorama
A panorama object consists of a CSV coordinate file and a panorama picture or panorama video file. In the CSV file, the coordinates of the panorama, the rotation values, and the panorama path are included. The coordinates and paths of multiple panoramas can be recorded in a single CSV file.

Lighting
Create lights in the scene, like spotlights, lighting, etc., to simulate the lighting effect in real life.
Tags
Create picture or text tagging objects in the scene.
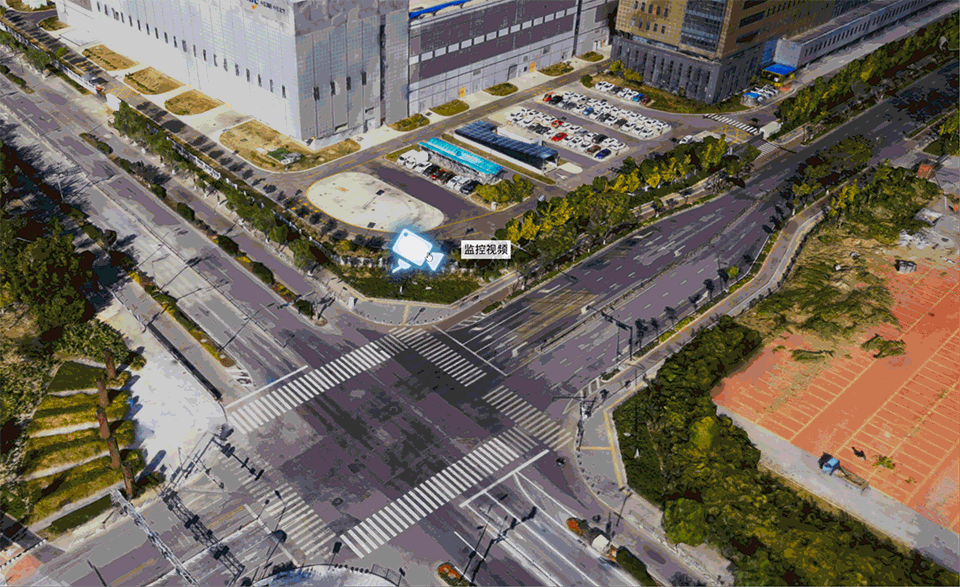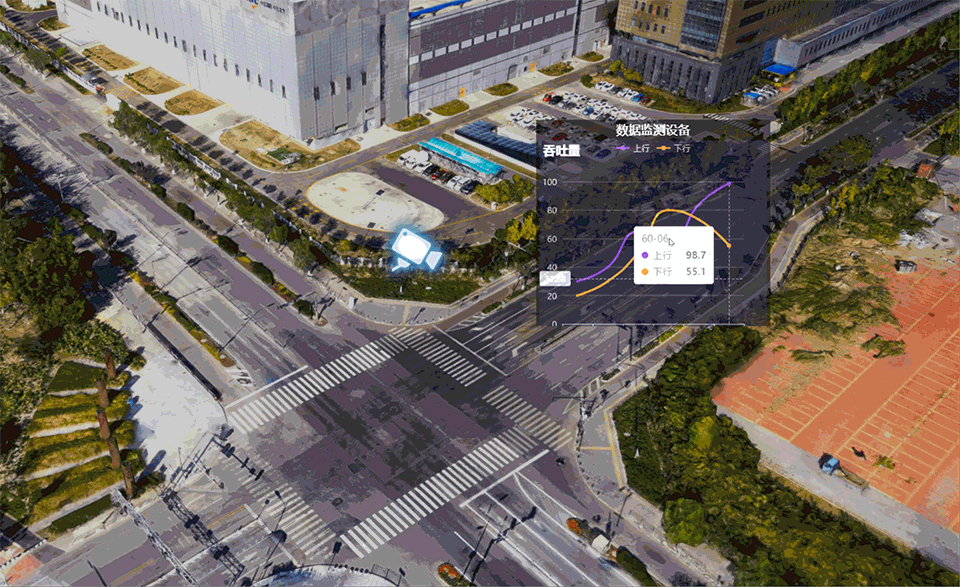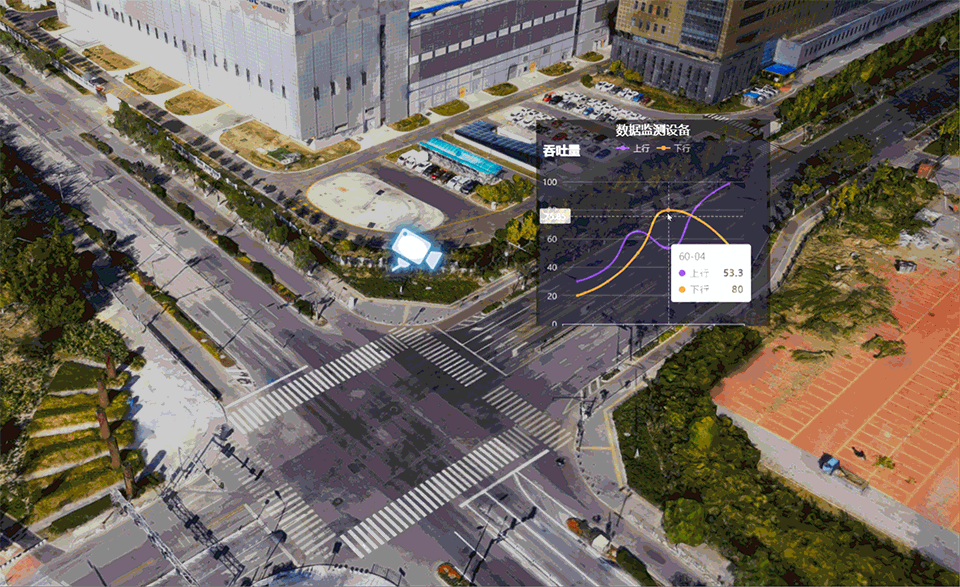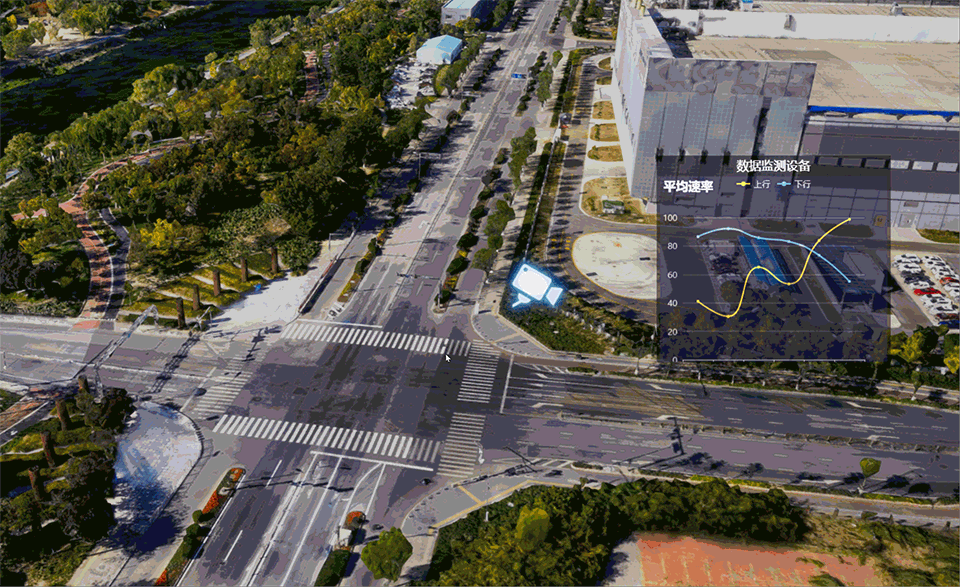
Dynamic markup
Add the effect of dynamic markup to the scene.
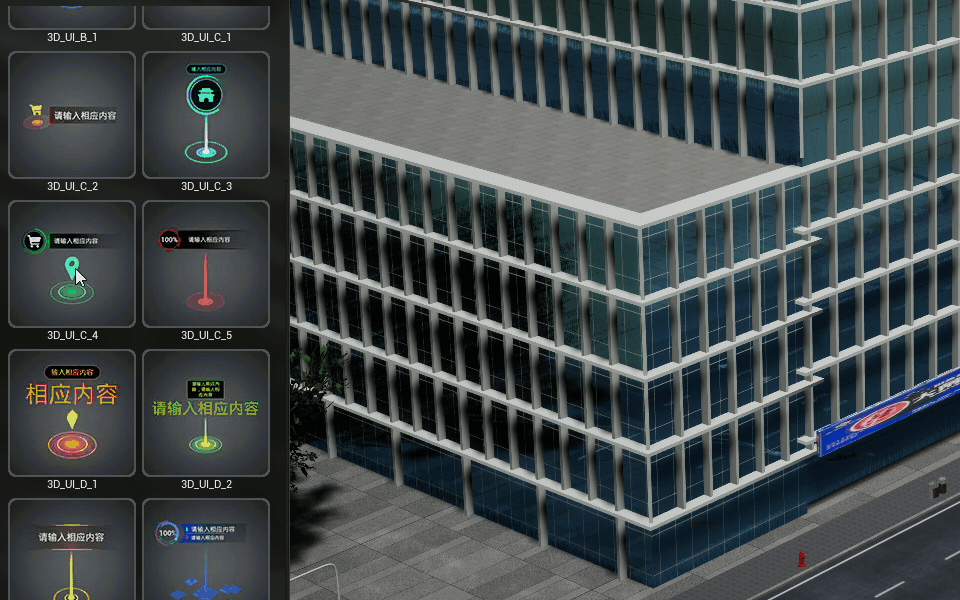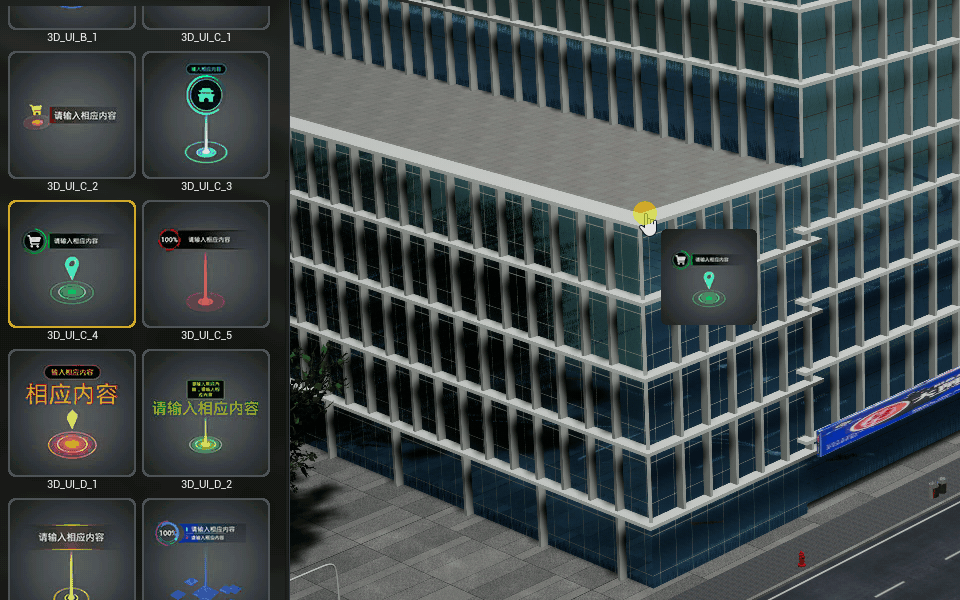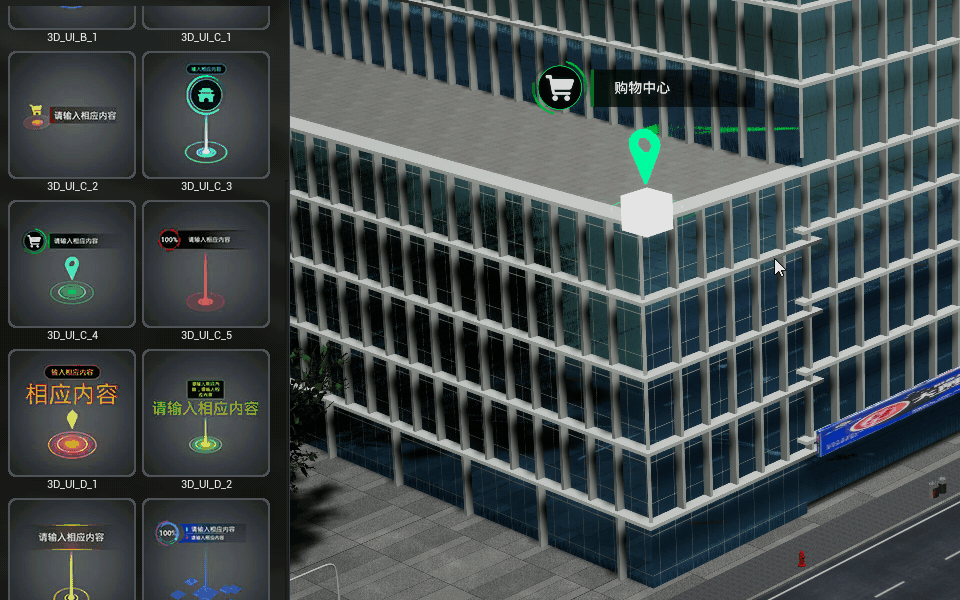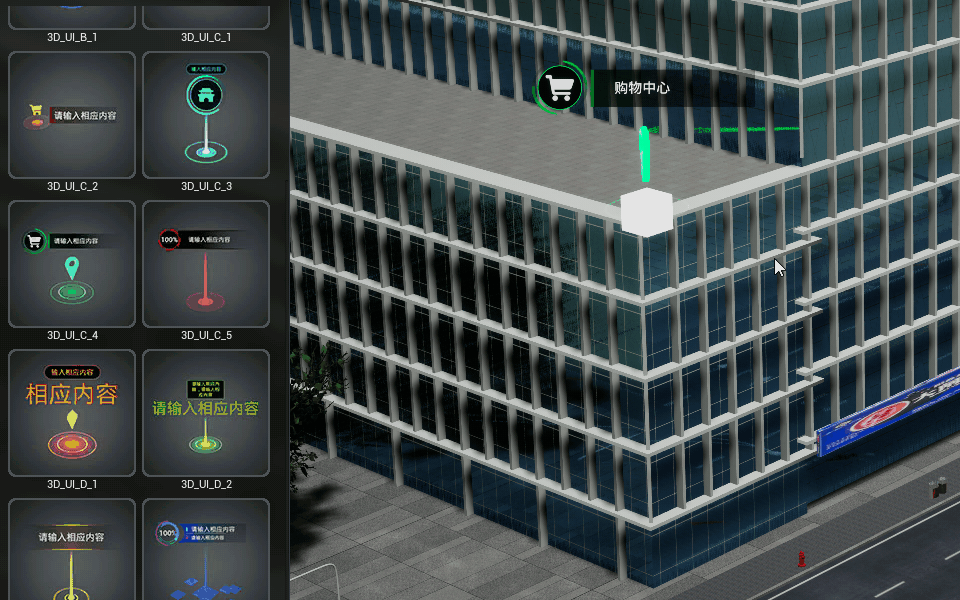
Decals
Can be mapped on the surface of objects in the scene.
Light flow
Can simulate the effect of light flow.
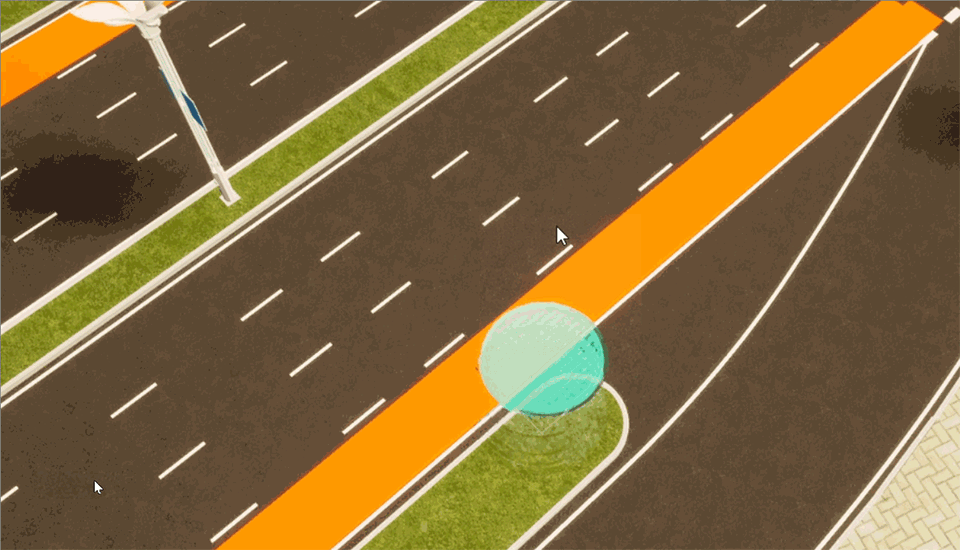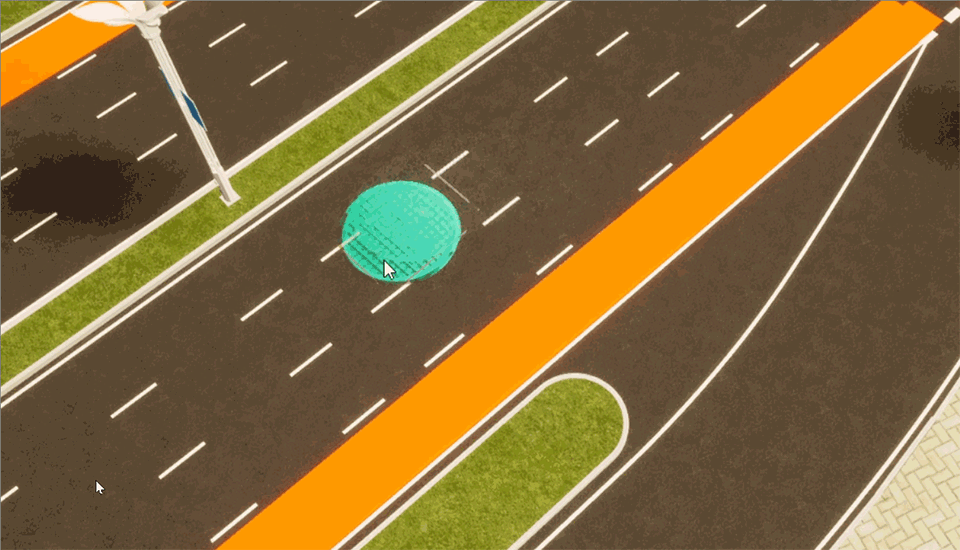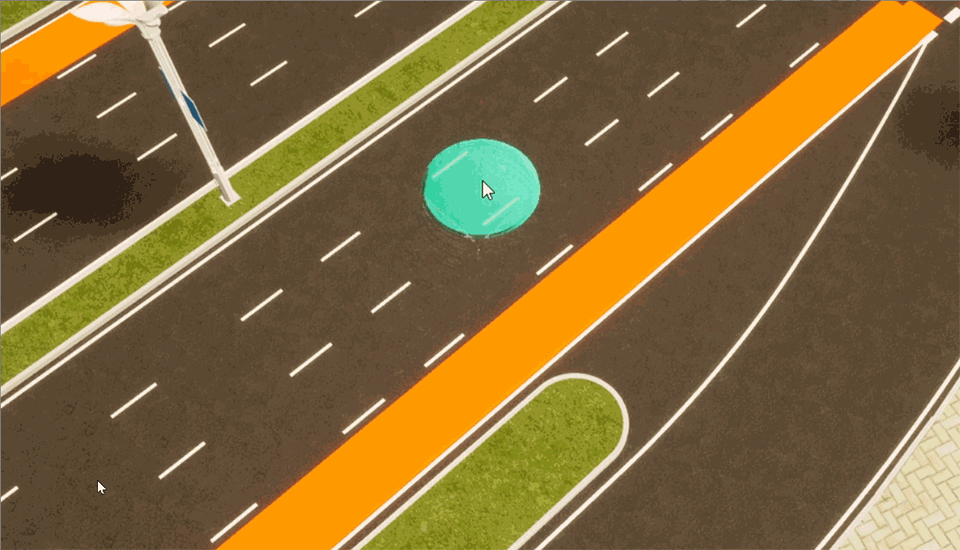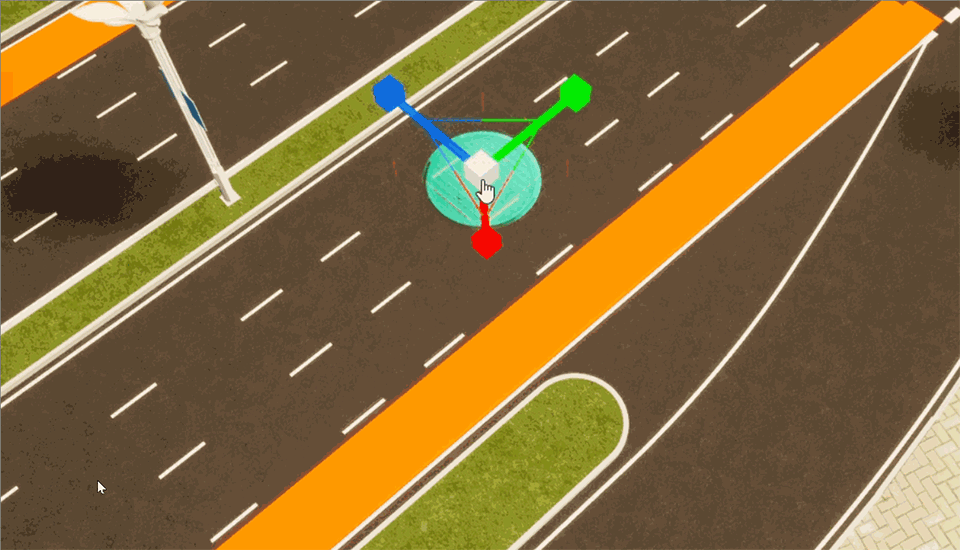
Radiant circles
Create an effect in the scene that simulates light radiation.

Polyline
Create a poly-line object in the scene.
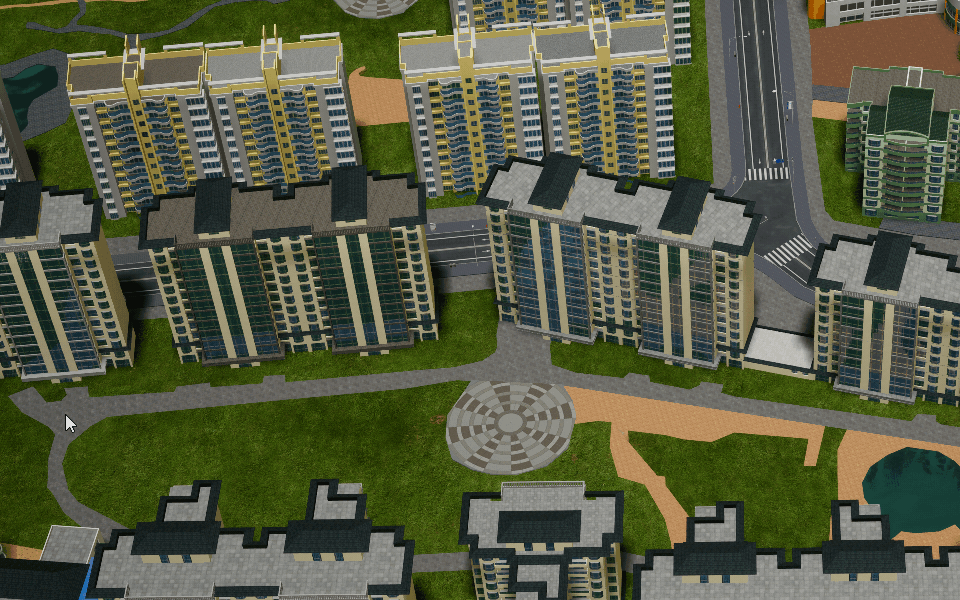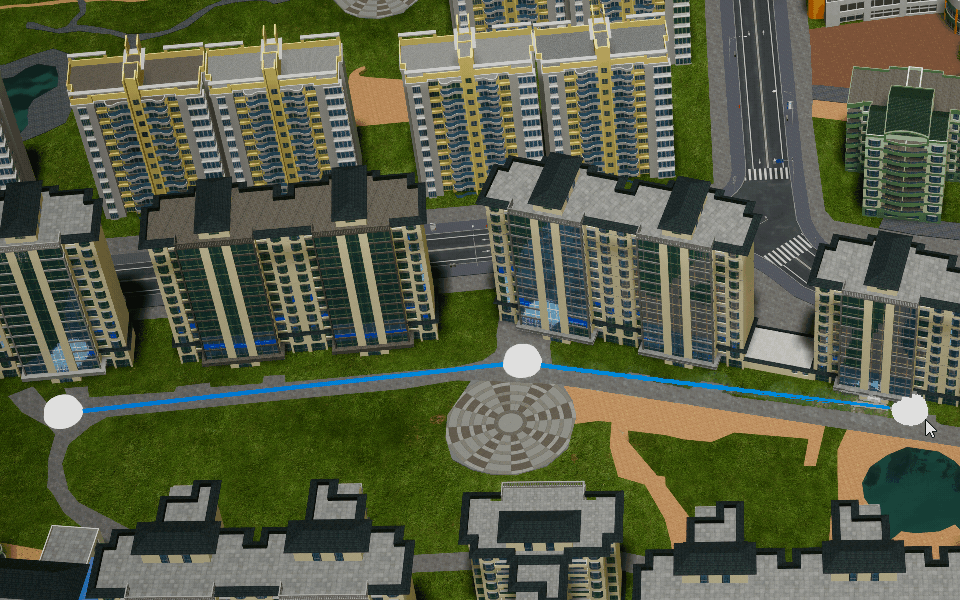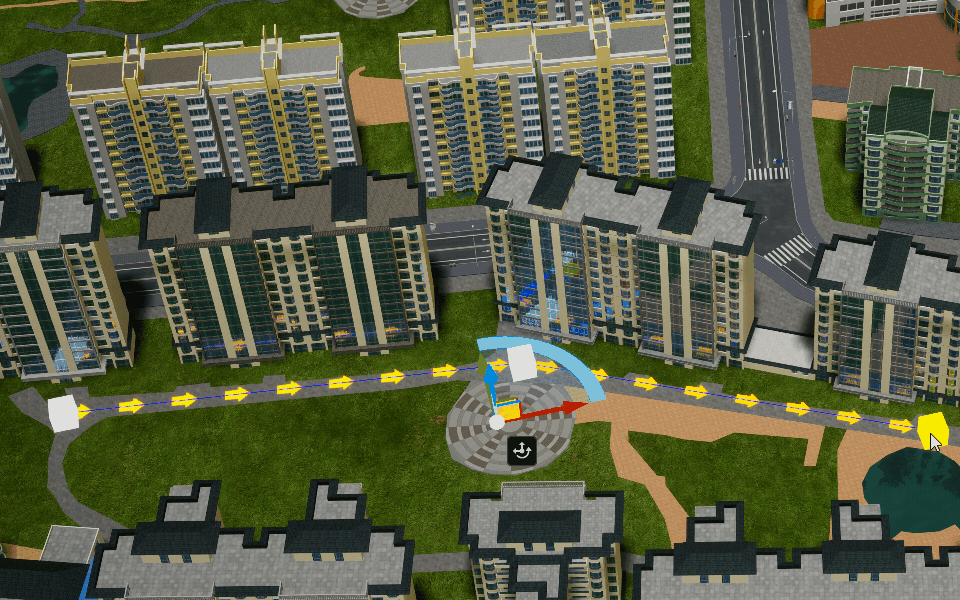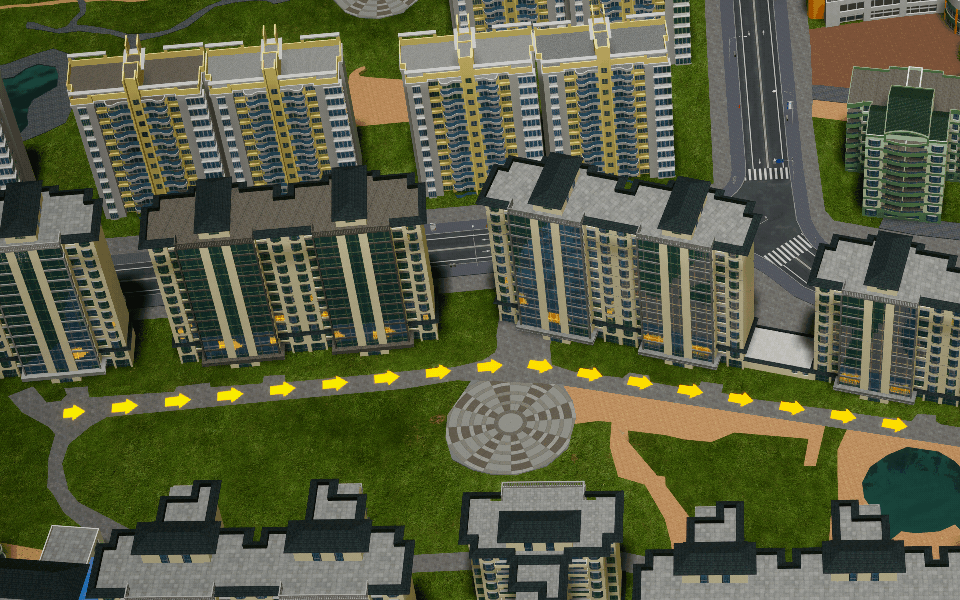
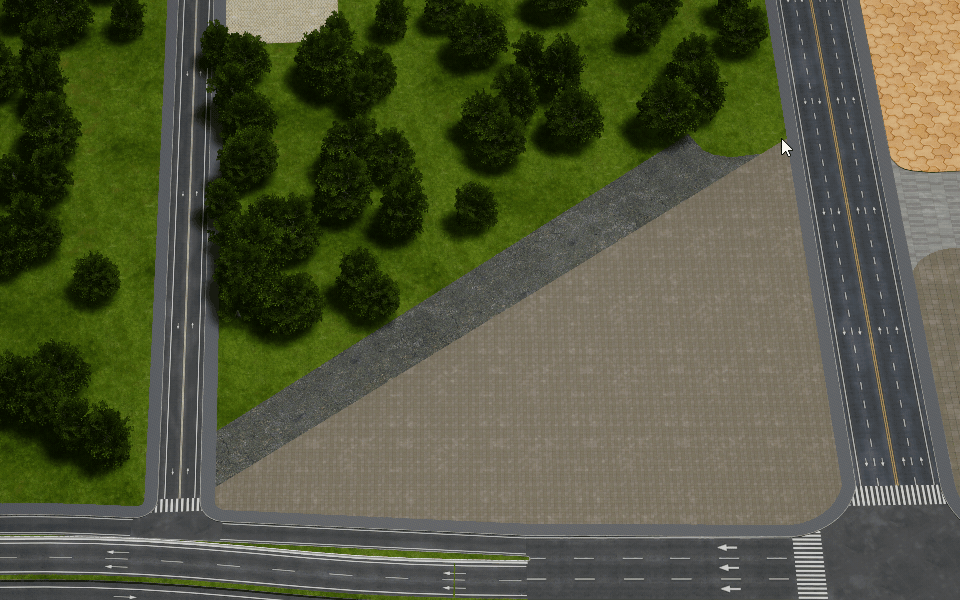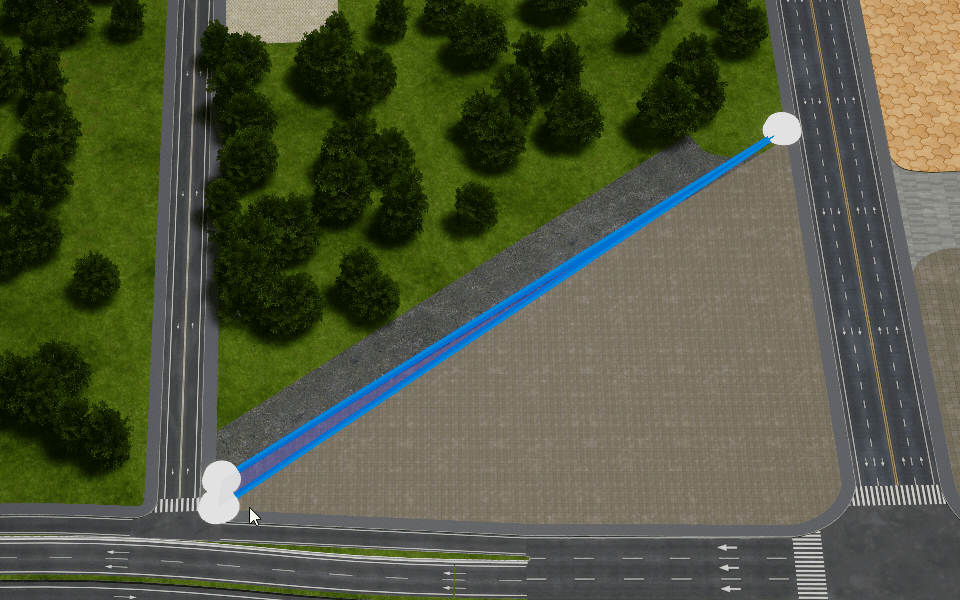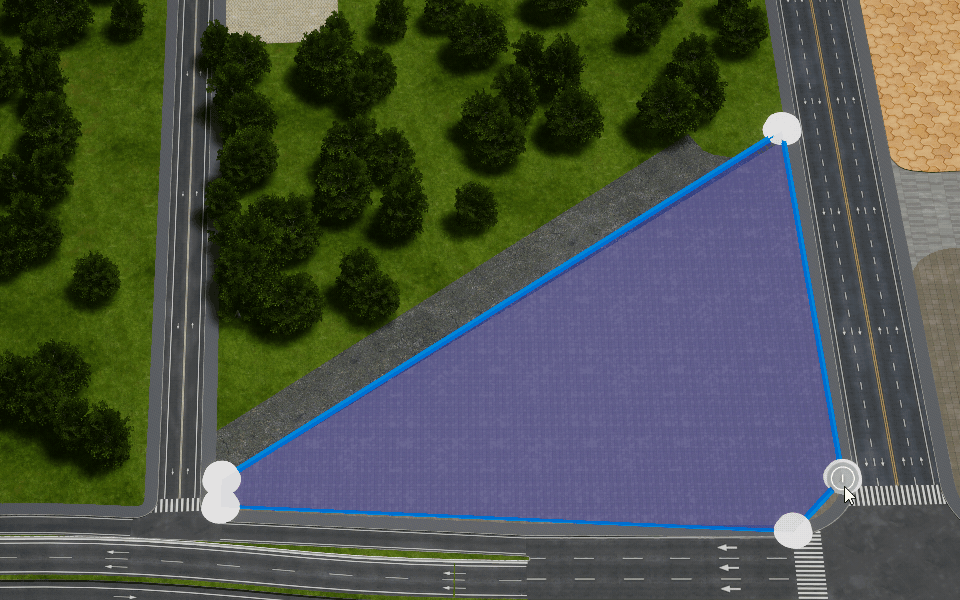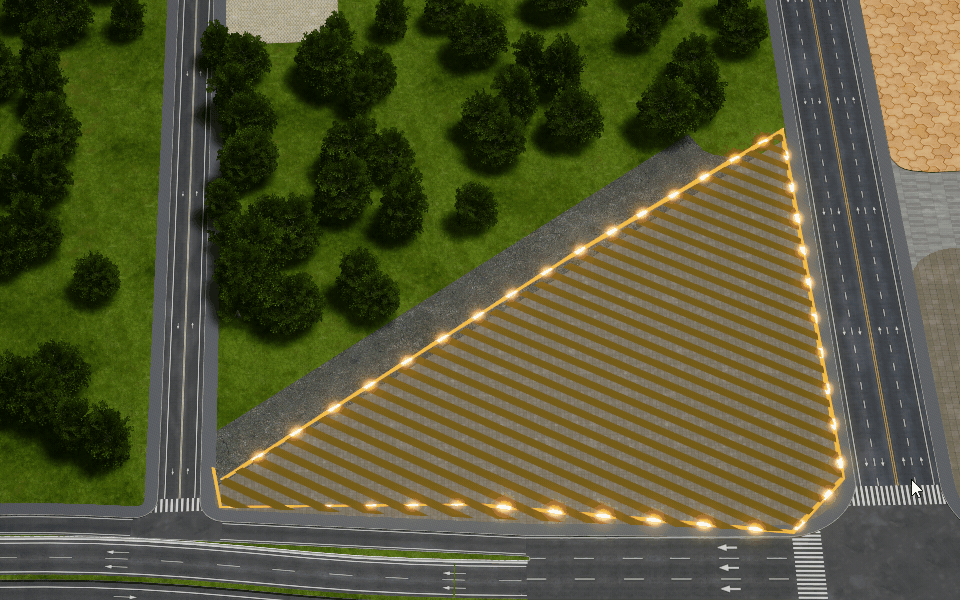
Polygon
Create a polygon object in the scene.
Publish a video streaming service
Instructions
The released project needs to be integrated first.
Enable/stop/debug services
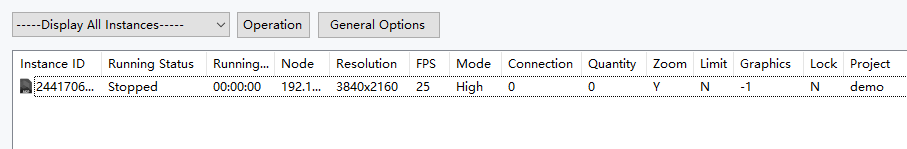
When the service settings, projects, render nodes, and instances are all set up, you can start or stop the service and other related actions.
Start: Start the Cloud service normally.
Stop: End all instance processes started. These include processes such as AirCityCloud.exe, SignallingWebServer, HttpServer, MatchServer, etc.
Debug: Right-click on the "Start" button to enter debug mode. Debug mode will bring up multiple command line Windows and 3D scene Windows. It is easy to develop and debug.
Publish a cloud rendering service
Launch the CloudMaster program on your master computer.
On the "Service Settings" page, set related parameters.
If you do not need to use the public network access service, do not set Trunk Service Configuration. You can skip the settings; all parameters will work with the default values.
On the Project List page, add one or more project paths.
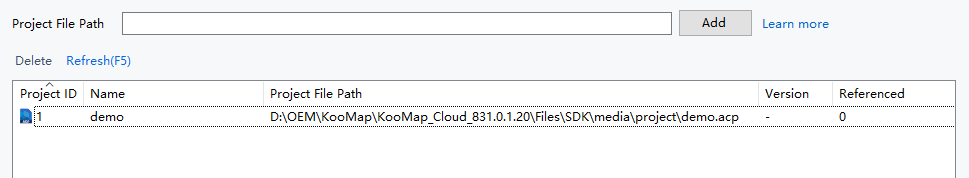
Select "Start" to start the service.
When you return to the master computer, you can see the corresponding contents in "Render Nodes" and "Instance List" in CloudMaster. If the corresponding content does not appear, shut down the service and start the service again.
In the "Instance List" page, select an instance and then select player to quickly preview the cloud service content.